Having a healthy body weight is a challenge for many, many people. Trying to maintain your ideal weight takes a combination of eating right, exercising regularly and being active.
But determining if you are at a healthy weight is not always about just the number on the scale. There are other means available to help each of us assess what weight is ideal for our height, age, gender and body type.
How Much Should I Weigh?
The CDC estimates 3/4 of the American population will likely be overweight or obese by 2020. The latest figures from the CDC as of 2014 show that more than one-third (36.5%) of U.S. adults age 20 and older and 17% of children and adolescents aged 2–19 years were obese.
Individuals who are obese are at a greater risk of developing diabetes, stroke, heart disease, high blood pressure, arthritis and some cancers. The risk factors for all these conditions go down when our weight is where it should be.
There are several ways to assess your body fat levels. Learn more by reading further about these measurement processes and what they can tell you. For a great video on this topic go to “How Much Should I Weigh?”
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is one of the most common means of calculating your body fat levels.
BMI does not measure body fat directly, but research has shown that BMI is moderately correlated with more direct measures of body fat. For most people BMI appears to be strongly correlated with various adverse health outcomes consistent with these more direct measures of body fatness.
BMI is a person's weight divided by their height (squared). A high BMI can be an indicator of high body fat content.
- BMI is less than 18.5, underweight range
- BMI is 18.5 to <25, normal
- BMI is 25.0 to <30, overweight range
- BMI is 30.0 or higher, obese range
Determine your BMI by finding your height and weight in this BMI Index Chart.
Waist-Hip Ratio (WHR)
A waist-hip measurement is the ratio of your waist measurement to that of your hips. You measure the smallest circumference of your waist, usually just above your belly button, and divide that total by the circumference of your hips at their widest part.
For example, if a woman's waist is 28 inches and her hips are 36 inches, her WHR is 28 divided by 36 = 0.77. Based on the categories below, she would be at low risk of having cardiovascular heath problems.
Below is a breakdown of WHR linked to risk of cardiovascular health problems.
For Men ….
- Less than 0.9 - low risk of cardiovascular health problems
- 0.9 to 0.99 - moderate risk of cardiovascular health problems
- 1 or over - high risk of cardiovascular problems
For Women ….
- Less than 0.8 - low risk of cardiovascular health problems
- 0.8 to 0.89 - moderate risk of cardiovascular health problems
- 0.9 or over - high risk of cardiovascular problems
Various studies have shown that people with apple-shaped bodies, who have larger WHRs, have higher health risks compared to people with pear-shaped bodies who have lower WHRs. An apple-shaped person will have more fat accumulating on the waist, while a pear-shaped person has the fat accumulating on the hips.
Although WHR does not accurately measure a person's total body fat percentage, or their muscle-to-fat ratio, it is a better predictor of ideal weight and health risks than BMI.
Waist-to-Height Ratio
Another measurement that has proven to be a better predictor of future heart disease and diabetes risk than BMI is waist-to-height ratio. Keeping your waist circumference to less than half your height can help increase life expectancy and overall quality of life. For instance:
- A man 6ft (72 inches, 183 cm) tall, should keep his waist measurement below 36 inches (91 cm)
- A woman 5ft 4 inches, i.e. 64 inches (163 cm) tall, should keep her waist measurement below 32 inches (81 cm)
In general it is recommended that women’s waistlines don’t exceed 35”; and men’s should be 40” or less.
Body Fat Percentage
Many experts believe that calculating people's body fat percentage is the best way to gauge their fitness level because it is the only measurement that includes the body's true composition.
Any male whose body fat percentage is over 25% or female over 31% is either overweight or possibly obese.
Your body fat percentage is the weight of your fat divided by your total weight. Many gyms and doctor's practices have devices that can tell you your body fat percentage.
The American Council on Exercise has established these ranges for Body Fat Percentages.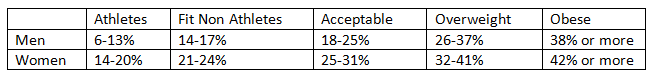
How Can We Help?
Blackbird Clinical Services offers Biometric Testing that will calculate Body Fat % and BMI, along with blood pressure, glucose/blood sugar and cholesterol levels. To learn more about this service go to Biometric Services and to discuss setting up an appointment go to Wellness Biometric Testing.